Back pain can be developed to anyone, even teens and children. Orthopedic injuries are the greatest risk factor for developing back pain. Besides there are many risk factors that develops low back pain. However, the following factors might put you in great risk of developing back pain:
Age :
Many studies have shown that the
risk of low back pain increases as a patient gets older, but once one reaches
the age of about 65 the risk stops increasing. Back pain is the most frequent
cause of the limitation of activity in people younger than 45 years of age.
Psychological, Social and Spiritual Factors :
It is increasingly recognized that a wide variety of psychological and social factors can increase the risk of low back pain. Research has shown that anxiety, depression, stressful responsibility, job dissatisfaction, mental stress at work, and substance abuse can place people at increased risk for developing chronic low back pain. Fear of pain, negative beliefs, sexual abuse, fear-avoidance and somatization symptoms (feeling sick without an actual disease) can also increase risk. Studies have also shown that single working mothers are at higher risk for low back pain. Spiritual factors, including a lack of meaning in life or lack of inner peace, may also predispose an individual to chronic back pain.
Excess weight :
Being overweight increases stress on the lower back, as well as other joints (e.g. knees) and is a risk factor for certain types of back pain symptoms.
Previous Back Injury :
The single best predictor of back pain is a previous back injury. As noted previously, relapses are common after a significant episode of low back pain.
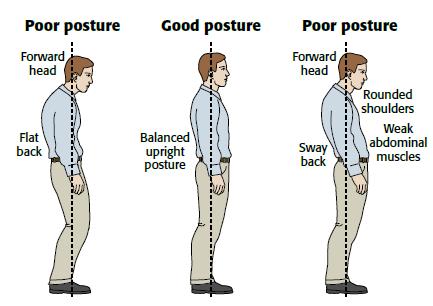
Poor Posture and Alignment :
Poor posture or improper alignment may predispose individuals to developing back pain over time as this can cause undue stress on certain areas of the back.
Occupational hazards :
Any job that requires repetitive bending and lifting has a high incidence of back injury (e.g., construction worker, nurse). Jobs that require long hours of standing without a break (e.g., barber) or sitting in a chair (e.g., software developer) that does not support the back well also puts the person at greater risk.
Genetics :
There is some evidence that certain types of spinal disorders have a genetic component. For example, degenerative disc disease seems to have an inherited component.
Gender :
The evidence here is confusing ! Some studies have shown that males are at greater risk for low back pain, while other studies suggest that females are more likely to develop this type of pain. Women who have had two or more pregnancies have a higher risk of developing low back pain.
Level of Activity (Physical Fitness) :
The strength and endurance of the back and abdominal muscles have been shown to be related to the development of back pain. Studies have shown that physical fitness and conditioning may help to prevent back injuries.
Lack of exercise :
Physical inactivity is a primary cause of most chronic diseases. Weak, unused muscles in your back might lead to back pain.
Smoking :
Studies have shown that smokers have a 1.5 to 2.5 times greater risk of developing low back pain than nonsmokers. It is thought this may be due to reduced oxygen supply to disks and decreased blood oxygen from the effects of nicotine on constriction of the arteries.
Alcohol and Drug Abuse :
Adverse health reactions can result from both alchohol & drugs. While chronic health problems are often associated with long-term misuse and abuse. Alcohol and illicit drug use have been shown to increase one's risk for low back pain.
Sports :
Sports such as skiing, snowboarding, sledding, tobogganing, gymnastics, wrestling and contact sports such as football and rugby increase the risk for developing low back pain as a result of injuries. These injuries can result in back pain whether through direct injury to the low back, or through injury to other parts of the body that cause abnormal stress on the low back.
Pregnancy :
Pregnant women are more likely to develop back pain due carrying excess body weight in the front, and the loosening of ligaments in the pelvic area as the body prepares for delivery.
Other factors :
There are many other factors those may play a part in the development of acute and chronic back pain. These include underlying spinal conditions such as osteoporosis, spondylolysis, discogenic disease, degenerative joint disease (osteoarthritis) of the spine, osteoporosis, and scoliosis
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Twitter
Twitter 1:08 AM
1:08 AM
 Zia
Zia




 Posted in
Posted in 



0 comments:
Post a Comment